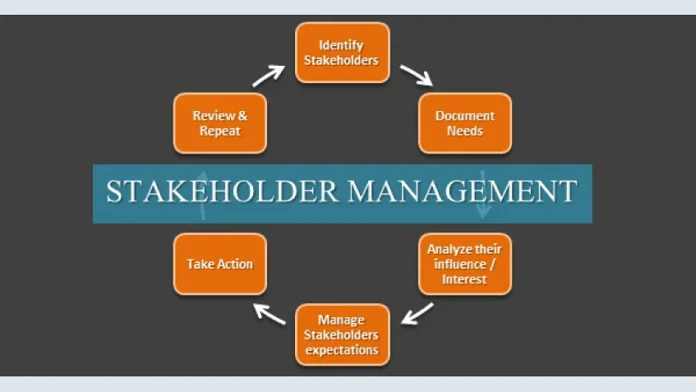
As a business owner, do you feel overwhelmed trying to manage all your stakeholders? Are you uncertain of how to effectively engage with the key players in your organization?
This article explores the fundamentals of stakeholder management to help guide you on your journey. You’ll learn how to identify and assess stakeholders, build relationships and align their interests with those of the organization. Unlock the power of stakeholder management and take control of your business today.
Identifying Stakeholders
Stakeholder management is the process of identifying and engaging stakeholders in order to understand their needs and expectations, address issues, and manage conflicts. Stakeholders can be internal or external to your project or organization, including people from all the disciplines involved in a project, individuals from other organizations, customers and end users. One important aspect of stakeholder management is complaint management, which involves identifying and addressing any concerns or grievances that stakeholders may have. By actively listening to and resolving complaints, organizations can build trust and strengthen relationships with their stakeholders.
Identifying them starts with having a list of names that represent key interest groups for your project. This list should include both those associated directly with the project (e.g., team members, sponsors) as well as those with an indirect interest (e.g., the local community affected by it). Consider the range of people who might be affected by or interested in your project’s outcome:
- Project team members
- Project sponsors
- People from related projects
- Executives and other decision makers
- Vendors/suppliers
- Stakeholders from other functional areas in the organization
- Local community members
- Regulators/legislators
- End users/customers
Analyzing Stakeholder Power and Influence
Knowing who holds the power is crucial for effective stakeholder management. In order to manage them, identified as either direct or indirect, entrepreneurs must understand their interests and needs in order to leverage and engage with them beneficially. Identifying the stakeholders’ level of influence over decisions, policies and strategies is key when deeping their engagement in business activities.
Analyzing their power can be a chore that requires time, research and analysis to understand who the powerful players are at different organizational levels and how they influence decisions within the organization. Power exists on different levels and may range from within a team or project team members will typically carry some degree of influence to C-level executives who are able to affect change throughout an entire organization. It’s important for enterprises to detect both formal and informal sources of power in order to address all stakeholders’ needs properly during their management processes.
By determining a key player’s level of interest in your activities, you will be able to gauge how dedicated they are towards successful engagement with your business efforts. Understanding their desired outcomes such as goals, values or power can help you decide how much effort should go into engaging with them. Additionally, determining sources of information that appeal to each person is another way you can ensure that what your delivering messages reaches those who could benefit from them most effectively -all while mitigating risks associated with potential miscommunication between potent players in the organization.
Developing Strategies for Engaging Stakeholders

When planning how to engage them, it’s important to consider the interests of all parties involved. This means determining who will be most impacted by the project or initiative, what types of communication are appropriate for specific individuals or groups, and how best to facilitate communication between stakeholders.
Their engagement can come in many forms: from informal conversations over coffee to more formal methods such as surveys or interviews. You may also choose to offer workshops or brainstorming sessions to solicit feedback from your stakeholders or establish focus groups that allow for the flow of ideas between different viewpoints and for the testing of responses to proposed solutions. Utilizing social media channels such as LinkedIn and Twitter may also be part of your strategy in fostering relationships with more distant colleagues; however these channels should be used selectively so as not to become a source of distraction when nothing urgent is being communicated.
Developing a plan that allows these types of opportunities while creating an atmosphere where stakeholder comments can be both heard and addressed is essential. It’s important not only that you understand what each one wants out at the end but also that they understand why your plans are necessary for achieving it – this will help build trust in you and your organization’s goals over time.
Measuring and Evaluating Stakeholder Engagement

In order to effectively manage and engage them, you need to measure and evaluate stakeholder engagement. Having a systematic way to measure and evaluate engagement will give you insight into the effectiveness of your engagement strategy and ways to improve it.
Your evaluation should be based on the level of engagement your stakeholders have with your organization and how their involvement impacts your overall strategy. It is important to consider both quantitative data (like survey results) and qualitative data (such as feedback from stakeholders).
Quantitative Measurements May Include:
- Surveys of stakeholders’ satisfaction with the organization’s communication policies, plans, programs, products, services or other initiatives
- Monitoring of online sentiment about the organization’s performance
- Reaching predetermined goals for engaged audiences on social media platforms
- Tracking changes in the number of clicks or visits to the organization’s website or social media page over time
- Evaluating response rates to surveys or other methods of outreach
Qualitative Measurements May Include:
- Meeting with stakeholders in person or through video chat technology
- Phone interviews with contingent employees, partners, suppliers and customers
- Analyzing verbal feedback at public events such as town hall meetings or open forums
- Clustering customer responses into themes in order to provide insights that guide action
Conclusion

By staying up-to-date on stakeholder communications, keeping them updated on the status of project deliverables, resolving any conflicts efficiently and so on, project team members can significantly improve the chances for success — forging strong relationships with stakeholders is not only essential in managing projects; it is also essential in driving business results.
Through regular communication with key players, organizations will build vital trust relationships that will enable them to work more successfully together in the future.