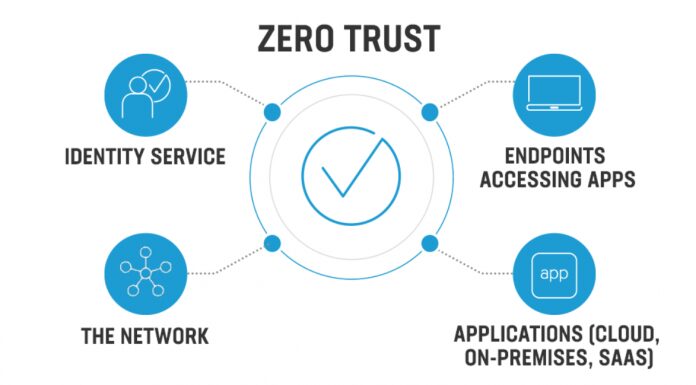
It recognized Zero Trust as a means to stop cyberattacks. But traditional security models and the idea of “all or all or nothing” have left many companies reluctant to embark on the Zero Trust journey. It is good to know that constructing Zero Trust architecture is much easier than it appears. Since Zero Trust is an augmentation of your current architecture it mustn’t be the complete overhaul of your technology. It can instead be implemented, allowing users to enjoy the technologies and tools that you already have.
We provide all information about how to implement a zero trust network.
By using a five-step approach to creating and maintaining Zero Trust, you can determine how to implement a zero trust network and what you need to do next.
Implementing zero trust is a method of never trusting, and verifying the authenticity and the privileges of users and devices, regardless of their location within the network. Zero trust is a result of security systems for network access control (NAC) systems and the division of your network by the areas you’re most likely to secure.
Once you’ve identified the assets that are most sensitive to attack and assets, you must determine how traffic flows through these areas of the network. After that, you can design your zero-trust strategy in line with this.
Problems with how to implement a zero trust network
Implementing zero-trust security requires a thorough awareness of the most typical challenges you might face. They include complicated infrastructures, costs, and the necessity for software that is flexible.
Complex Infrastructure
For many organizations, their infrastructure consists of many servers, proxies, databases, internal applications, and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions. Certain of these could be in the cloud, while others are hosted on-premises. Secure each component within your networks, and being able to meet the requirements of on-premises or cloud environment, could pose many challenges.
Furthermore, you might be trying to protect systems that are made up of a mixture of new and old technology and software. All these components can cause many issues in ensuring that you have complete zero-trust security.
Cost and effort
To establish zero-trust, it might have to commit time as well as financial and human resources. Deciding how to divide your network and determine who should have access to what areas take meticulous planning and collaboration. You must then determine the most efficient methods of confirming the authenticity of each device and user before they are granted access.
The human ability to do this will must significant amounts of money, especially in the absence of an infrastructure that, as a design, is well integrated with your surroundings.
Flexible Software
One of the most important factors to be considered when deciding the best way to set up a zero-trust network is the adaptability of the software that runs the system. It is possible to integrate various micro-segmentation software, identity-aware proxy servers, and software-defined boundaries (SDP) tools.
Without flexible software, it is possible to buy more security systems to guard all the elements of your surroundings. With the flexibility of a system, you can simplify the development and implementation of your zero-trust security system.
Five steps to how to implement a zero trust network
The zero trust guidelines can assist you how to implement a zero trust network establishing and putting in place your zero-trust cybersecurity framework. They can assist you in establishing an effective data loss prevention (DLP) and breach prevention strategy. The following is a concrete step-by-step guide for zero trust.
Definition of the Attack Surface
The definition of the attack zone is the most important step on your zero trust checklist. To do this, you must concentrate on the areas you want to guard. In this way, you’ll not be overwhelmed when setting up policies or deploying tools throughout your network. Concentrate on the most important digital assets.
Sensitive data
This includes information of employees and customers as well as confidential data that you do not wish to be in the hands of a burglar.
Essential Applications
These are the software applications that play an integral function in your most vital business procedures.
Physical Assets
Physical assets are anything in value from point-of-sale (PoS) terminals to Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices to medical equipment.
Corporate Services
This includes the components of your infrastructure that help support the day-to-day activities of executives and employees and the components that support interaction and sales.
Put in place Controls Around Network Traffic
The flow of traffic through your network can be influenced by the dependencies that every system has. For example, many applications must access databases that contain customer, product, or service data.
So, requests do not “go through the network.” They must be directed through a database that contains sensitive and delicate information as well as a structure. Understanding the specifics will allow you to decide what network controls you want to put in place and how to place them.
Design a zero trust network
Zero trust networks are constructed around your particular protection surface — there is no one-size-fits-all solution. In the majority of cases, the architecture you choose to build may start with the use of a Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW), which could serve as an instrument for separating certain areas of your network. At some point, you’ll need to introduce multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure the security of users before being allowed access.
Make a zero trust Policy
Once you’ve designed the network, you’ll be required to develop Zero Trust policies. It is best to do this by using The Kipling Method. This is the process of asking who is who, what, when, which location, how, and in what way for each device, user, and network seeking access. It is best for how to implement a zero trust network.
Watch Your Network
Monitoring your network’s activity could help you identify possible issues earlier and give valuable insight to improve network performance without risking security.
Reports
The reports that are produced on a regular or continuous basis could be used to detect irregular behaviors. It is also possible to analyze them to see the extent to which your zero trust system affects the performance of your employees or system and how you are better able to improve it.
Analytics
Analytics collects data from your system and offers information about how the system performs. Analytics are useful when you want to keep track of the network’s traffic and the performance of the elements of the network and patterns in user behavior.
Logs
The logs created by your system will provide you with permanent, time-stamped records of activities. They can be examined in a manual manner or by using analytical tools, like machine learning algorithms that recognize patterns and patterns.
Read More: Dropbox can’t establish secure internet connection.
Learn more how to implement a zero trust network read this post full find Selfoy.com on google.com .